Macroscopic and microscopic morphology of the gonads of Peltophryne empusa (Anura: Bufonidae)
Main Article Content
Abstract
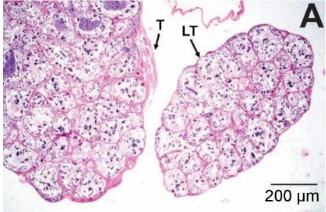
The goal of this study is to make a macroscopic and microscopic description of the gonadal morphology of Peltophryne empusa. To do so, six specimens (two males and four females) were collected during the two seasons (dry and wet) of the period 2018-2019 in San Paúl, Artemisa, Cuba. Specimens were anesthetized with a diethyl-ether 99% solution, then, they were sized and measured. After that they were dissected and the entire masculine gonads and part of the feminine ones were taken and fixed in formaldehyde 4% and glutaraldehyde 2.4% solutions to be processed by optical and electronic microscopy respectively. Masculine gonads consisted in two elongated non pigmented and very lobulated testicles and two Bidder’s organs located in cephalic position. Feminine one had no Bidder’s organ. Several cysts with sexual cells in different stages of the spermatogenesis were found in the testicles such as: spermatozoa, spermatids, spermatocytes, Sertoli cells and connective tissue. Bidder’s organ consisted in previtellogenic oocytes, atresic bodies and fat tissue. Spermatozoa were formed by a head, a tail and an undulant membrane. Previtellogenic and vitellogenic oocytes, as well as atresic bodies and germinal bed were found in the ovaries. Oocytes were divided in an animal and a vegetal pole, the nucleus contained nucleoli and lamp brush chromosomes. These characteristics are similar to those of other are also found in other Cuban and foreign anurans. The presence of reproductive characteristics during the dry season in females might have been due to the high precipitations at the beginning of that season.
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
Los resultados publicados en la revista Poeyana se presentan bajo la Creative Commons Attribution License, que permite a cualquier lector hacer un uso libre de estos mientras refiera la fuente. No debe, por tanto, incluirse ningún material que no pueda ser publicado bajo estos términos, por ejemplo, fotografías con Copyright. Todos los datos o materiales extraídos de un trabajo escrito por otra persona, se deben identificar con claridad y atribuirse a sus autores, aunque no se hayan publicado o no se hayan citado palabra por palabra.
References
Alonso-Bosch, R. y L.Y. García-Padrón. 2017. Anfibios. Pp. 348-375. En: Diversidad biológica de Cuba: métodos de inventario, monitoreo y colecciones biológicas (C.A. Mancina y D.D. Cruz, Eds.). Editorial AMA, La Haban, 502 pp.
Alonso, R., A.J. Crawford y E. Bermingham. 2012. Molecular phylogeny of an endemic radiation of Cuban toads (Bufonidae: Peltophryne) based on mitochondrial and nuclear genes. Journal of Biogeography 39(3): 434-451.
Bishop, P.J., A. Angulo, J.P. Lewis, R.D. Moore, G.B. Rabb, y J.G. Moreno. 2012. The Amphibian Extinction Crisis-what will it take to put the action into the Amphibian Conservation Action Plan?. S.A.P.I.E.N.S. Surveys and Perspectives Integrating Environment and Society. 5(2): 97-111
Boisvert, F.M., S. van Koningsbruggen, J. Navascués y A.I. Lamond. 2007. The multifunctional nucleolus. Nature reviews Molecular cell biology 8 (7): 574.
Brown, F.D., E.M. Del Pino y G. Krohne. 2002. Bidder's organ in the toad Bufo marinus: effects of orchidectomy on the morphology and expression of lamina‐associated polypeptide 2. Development, growth & differentiation 44(6): 527-535.
Colombo, L., y P.C. Belvedere. 1980. Steroid-hormone biosynthesis by male bidders organs of the toad Bufo Bufo (L). General and comparative endocrinology 40(3): 320-321.
Farias, C.F., S.P. Carvalho-e-Silva y L. de Brito-Gitirana. 2002. Bidder's organ of Bufo ictericus: a light and electron microscopy analysis. Micron 33(7-8): 673-679.
Ferreira A., y M. Mehanna. 2012. Seasonal testicular changes in Dendropsophus minutus Peters, 1872 (Anura, Hylidae). Biocell 36(2):57-62.
Gilbert, S.F. 2013. Developmental Biology. Tenth Edition. Sinauer Associated Inc. 719 pp.
Harms, J.W. 1921. Verwandlung des Bidderschen Organs in ein Ovarium beim Mánnchen von Bufo vulgaris Laur. Zoologischer Anzeiger 53: 253-265.
Huang, W.S., J.Y. Lin, y J.Y.L Yu. 1996. The male reproductive cycle of the toad, Bufo bankorensis, in Taiwan. Zoological Studies. 35: 128-137.
Kidov A.A., K.A. Matushkina, S.A. Blinova y K.A. Afrin. 2017. Laboratory Reproduction of the Cuban Toad, Peltophryne empusa (Cope, 1862). Current Studies in Herpetology 17: 36-43
King, H.D. 1908. The structure and development of Bidder's organ in Bufo lentiginosus. Journal of Morphology 19(2): 439-468.
Montezol, M., M. Cassel, D. Silva, A. Ferreira y M. Mehanna. 2018. Gametogenesis and reproductive dynamics of Rhinella schneideri (Anura: Bufonidae): Influence of environmental and anthropogenic factors. Acta Zoologica 99(1): 93-104.
Myers, N., R.A. Mittermeier, C.G. Mittermeier, G.A. Da Fonseca, y J. Kent. 2000. Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403(6772): 853.
Pereda, J.A. 2017. La crisis biológica de los anfibios: los vertebrados más amenazados. El Ecologista 81: 21-23
Piprek, R. P., M. Klo y J.Z. Kubiak. 2015. Bidder’s organ-structure, development and function. International Journal of Developmental Biology 58(10-11-12): 819-827.
Pough F.H., R.M. Andrews, J.E. Cadle, M.L. Crump, A.H. Savitzky, K.D. Wells. 2001. Reproduction and Life History. Pp 228-259 En: Herpetology. Prentice Hall New York. 726 pp.
Pounds, J.A., M.R. Bustamante, L.A. Coloma, J.A. Consuegra, M.P. Fogden, P.N. Foster y S.R. Ron. 2006. Widespread amphibian extinctions from epidemic disease driven by global warming. Nature 439(7073): 161.
Pregill, G. 1981. Cranial morphology and the evolution of West Indian toads (Salientia: Bufonidae): resurrection of the genus Peltophryne Fitzinger. Copeia 1981: 273-285.
Rivalta, V., L. Rodríguez-Schettino, C.A. Mancina y M. Iturriaga. 2014. Amphibians of Cuba: checklist and geographic distributions. Smithsonian Herpetological Information Service 145: 1-48.
Rodríguez, Y., A.S. Ochotorena, M.D.L.S. Valdés y R. Lara. 2015. Gametogenesis Stages of Cuban Eleutherodactylus Frogs Revealed by TEM Studies. [Inédito]. 2 pp.
Sanz A., Y. Rodríguez, M. de L. Segura, R. Lara, y L.F. Jimenez. 2015. El órgano de Bidder en sapos (Peltophryne spp.) endémicos de Cuba. Aspectos morfológicos y de ultraestructura. Revista Cubana de Ciencias Biológicas 4(1): 78-88.
Sanz Ochotorena, A. C., Y. Rodríguez Gómez, M. de L. Segura-Valdez, R. Lara Martínez y L. F. Jiménez García. 2019. Atlas de la morfología microscópica de las gónadas de anfibios y reptiles de Cuba. La Habana, Editorial UH. 176 pp.
Sanz, A., Y. Rodríguez, M. de L. Segura-Valdez y L.F. Jimenez. 2007 Ultrastructure of spermiogenesis in Bufo fustiger (Anura: Bufonidae). Acta Microscópica 16 (1-2) suplemento 2: 1-2.
Sanz, A., Y. Rodríguez, M. de L. Segura-Valdez, L.F. Jimenez y M. Iturriaga. 2007. Gametogenesis in cuban amphibians. Acta Microscopica 16 (1-2) suplemento 2: 1-2.
Sanz, A., Y. Rodríguez, M. de L. Segura-Valdez, R. Lara, y L.F. Jimenez. 2008. Estructura y ultraestructura de la gónada de los machos de Bufo fustiger (Anura: Bufonidae). TIP. Revista especializada en ciencias químico-biológicas 11(2): 81-86.
Scaia, M.F., E. Regueira, A.G. Sassone, M.C. Volonteri y N.R. Ceballos. 2011. The Bidder's organ of the toad Rhinella arenarum (Amphibia, Anura). Presence of steroidogenic enzymes. Journal of Experimental Zoology Part A: Ecological Genetics and Physiology 315(8): 439-446.
Sretarugsa, P., W. Weerachatyanukul, J. Chavadej, M. Kruatrachue y P. Sobhon. 2001. Classification of developing oocytes, ovarian development and seasonal variation in Rana tigerina. Science Asia 27: 1-14.
UICN. 2011. IUCN Red list of threatened species. Versión 2011. 2. Disponible en http://www.iucnredlist.org/. Último acceso: 28 de noviembre de 2011
Wake, D.B. y T.V. Vance. 2008. Are we in the midst of the sixth mass extinction? A view from the world of amphibians. PNAS. 105 (1): 11466-11473